Does IV Therapy Help With Hangovers? Here’s What Actually Works
Waking up after a night of drinking with a pounding headache, nausea, and fatigue sends many people searching for fast relief. IV therapy has emerged as a popular option in wellness clinics and mobile services, promising rapid hangover recovery through direct nutrient delivery. But does this treatment actually work, or is it an expensive placebo? Let’s break down the science and explore what genuinely helps your body recover.
Key Takeaways
- IV therapy can ease some hangover symptoms—primarily dehydration, nausea, and headache—but it’s not a magic hangover cure and doesn’t reverse alcohol’s effects on your brain or liver function.
- For most mild to moderate hangovers, oral hydration with electrolyte drinks, rest, food, and time work nearly as well as IVs without the cost ($150-300 per session) or needle stick.
- IV treatment makes the most sense when someone is severely dehydrated, experiencing persistent vomiting, or cannot keep fluids down—and should always be administered with medical oversight.
- Evidence-based strategies that actually work include rehydration with water or sports drinks, NSAIDs like ibuprofen for pain, light food, and quality sleep.
- The only true hangover cure is prevention: limiting alcohol consumption, pacing drinks, choosing lighter-colored alcohols, and eating before and during your night of drinking.
What Causes Hangovers In The First Place?
A hangover is your body’s multi-system reaction to alcohol’s toxic byproducts, dehydration, and disrupted sleep. These effects typically peak 6-12 hours after your blood alcohol level returns to zero, leaving you feeling worse than you did while actually drinking.
Dehydration and Fluid Loss
Alcohol blocks vasopressin (also called ADH), the hormone that tells your kidneys to retain water. Without this signal, you urinate far more than you normally would—research shows alcohol causes approximately 4x the urine output compared to water. This leads to significant fluid and electrolyte loss, resulting in that familiar dry mouth, headache, and dizziness the morning after.
Toxic Byproducts and Liver Stress
When your liver processes alcohol, it first converts it to acetaldehyde—a compound that’s actually more toxic than alcohol itself. This substance triggers inflammation throughout your body, causing that “poisoned” feeling, nausea, and general malaise. Your liver then breaks acetaldehyde down further into harmless compounds, but this process takes time. Heavy drinking can deplete 100-200mg of magnesium per session, adding to your symptoms.
Inflammation and Immune Response
Studies show that alcohol triggers increased inflammatory markers in your bloodstream, similar to what happens when you’re fighting an infection. This contributes to body aches, fatigue, and that general “hit by a truck” sensation.
Sleep Disruption and Blood Sugar
Even though alcohol might help you fall asleep faster, it fragments your sleep cycles and reduces REM sleep—the restorative phase your brain needs. Alcohol also interferes with blood sugar regulation overnight, potentially causing hypoglycemia that worsens morning shakiness, brain fog, and weakness.
The Congener Factor
Darker spirits like bourbon, brandy, and red wine contain more congeners—byproducts of fermentation that your body must also metabolize. Research links higher congener content to more severe hangover symptoms, which is why clear liquors like vodka and gin tend to produce milder aftereffects.
Common Hangover Symptoms (And What’s Actually Going On)
Hangover symptoms typically begin 6-8 hours after you stop drinking and can vary dramatically from person to person. Understanding what’s driving each symptom helps explain why certain remedies work better than others.
| Symptom | Primary Cause | What’s Happening |
|---|---|---|
| Pounding headache | Dehydration, inflammation | Blood vessels dilate; brain tissue shrinks slightly from fluid loss |
| Nausea/vomiting | Stomach irritation, acetaldehyde | Alcohol inflames stomach lining and delays gastric emptying |
| Extreme thirst, dry mouth | Fluid loss | Your digestive system signals desperate need for rehydration |
| Fatigue and weakness | Poor sleep, low blood sugar | Disrupted rest cycles and depleted energy stores |
| Light/sound sensitivity | Nervous system irritation | Neuroinflammation heightens sensory responses |
| Muscle aches | Inflammation, electrolyte imbalances | Depleted magnesium and potassium affect muscle function |
| Irritability, anxiety | Brain chemistry disruption | Alcohol impairs normal neurotransmitter balance |
Factors That Make Symptoms Worse
Several variables influence hangover severity:
- Empty stomach drinking accelerates alcohol absorption
- Rapid consumption overwhelms your liver’s processing capacity
- High-congener drinks add to metabolic burden
- Lower body weight means higher blood alcohol per drink
- Genetic differences in alcohol-metabolizing enzymes (like ALDH2 variants) slow acetaldehyde clearance
- Nutrient status—people with adequate zinc, magnesium, and B vitamins often report milder symptoms
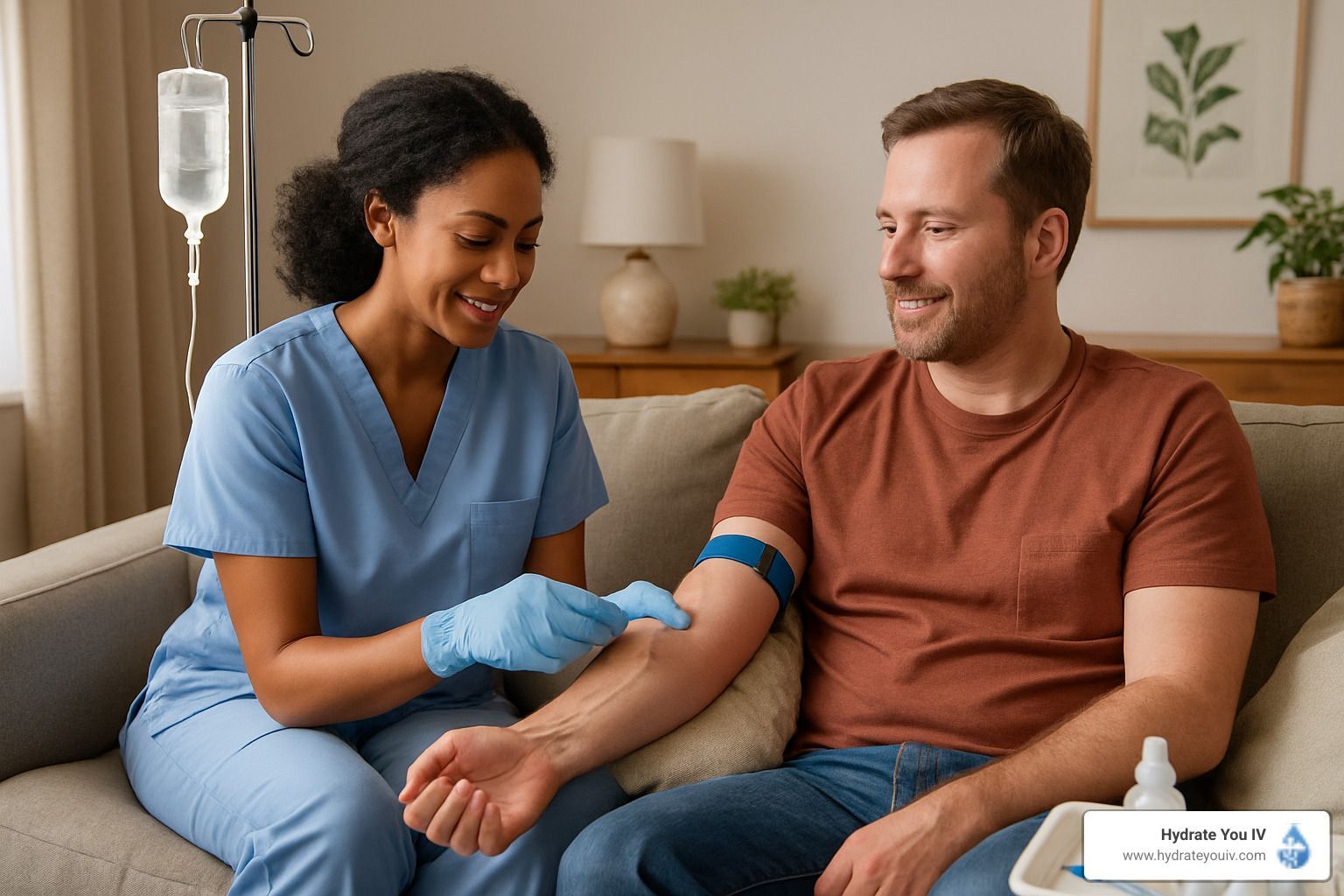
Does IV Therapy Really Help With Hangovers?
Here’s the direct answer: IV therapy can help relieve some hangover symptoms more quickly by rehydrating your body and delivering medications, but it does not “cure” or erase the hangover. Your liver still needs time to fully process alcohol metabolism byproducts.
What a Typical Hangover IV Drip Includes
Most IV vitamin therapy formulations for hangovers contain:
- 500-1000ml sterile saline or lactated Ringer’s solution
- Electrolytes (sodium, potassium, chloride)
- B complex vitamins (B1, B6, B12)
- Vitamin C
- Optional medications: anti-nausea drugs (ondansetron/Zofran) or NSAIDs (ketorolac/Toradol)
How IV Drip Therapy Works
IV fluids and nutrients bypass your digestive system entirely, going straight into your bloodstream for 100% bioavailability. This matters when someone is too nauseated to drink fluids or take pills orally. The efficient delivery method can provide rapid relief for dehydration-related symptoms within 30-45 minutes.
Expectations vs. Reality
You may notice faster improvement in headache, dizziness, and dry mouth after IV hydration therapy. However, your brain still needs time to restore normal chemistry, your liver continues processing toxins, and your sleep debt remains unpaid. A study in the Journal of Emergency Medicine found that IV fluids did not significantly shorten overall recovery time or reduce nausea and headaches compared to standard care in acutely intoxicated patients.
Safety Considerations
IV treatment is a medical procedure with real risks, including:
- Vein irritation or bruising
- Site infections
- Electrolyte imbalances (dangerous for those with kidney issues or high blood pressure)
- Fluid overload (risky for heart patients)
- Rare allergic reactions to additives
Always ensure intravenous treatment is administered by licensed professionals using sterile equipment.
The Placebo Effect
Part of the perceived benefit from hangover IVs may come from the rest period, professional attention, and expectation of improvement—research suggests 20-30% of symptom reduction may be attributable to fluids alone rather than the full “cocktail.”

What’s In A Hangover IV Bag (And What Each Component Does)
Not all hangover IV drips are identical, but most combine fluids, electrolytes, vitamins, and occasionally medications. Here’s what each component targets:
IV Fluids and Electrolytes
The foundation of any hangover IV is 500-1000ml of saline or lactated Ringer’s solution. This rapidly expands blood volume, improves circulation, and addresses the dehydration caused by alcohol’s diuretic effects. Electrolyte replenishment restores the sodium and potassium lost through excessive urination, aiding muscle function and reducing headaches.
B Complex Vitamins
B1 (thiamine), B6, and B12 support energy production pathways and nervous system function. Alcohol depletes B vitamins significantly, so replenishment may help reduce fatigue and brain fog. These essential vitamins are particularly important for hangover sufferers who drink frequently.
Vitamin C
This water-soluble antioxidant may help neutralize some oxidative stress from alcohol metabolism and support immune defenses. While the evidence for direct hangover benefit is supportive rather than definitive, vitamin C contributes to overall well being during recovery.
Magnesium
Alcohol can significantly deplete magnesium stores—up to 100-200mg per heavy drinking session. Replenishment may help with muscle cramps, tension headaches, and sleep quality, supporting various bodily functions during recovery.
Glutathione
Marketed as a “detox” ingredient, glutathione is a major antioxidant produced in your liver that helps detoxify acetaldehyde. IV glutathione may support liver function, but research on direct hangover benefit remains limited.
Medications
Some providers add prescription medications:
- Ketorolac (Toradol): An NSAID that reduces pain and inflammation
- Ondansetron (Zofran): Controls nausea and vomiting
These have contraindications—Toradol shouldn’t be used with certain medical conditions, and both require medical oversight.
A reputable IV provider should tailor ingredients to your health history, exercising caution with electrolytes for kidney or heart disease patients, checking for medication allergies, and screening for pregnancy.
IV Therapy vs. Simple Hydration: How Much Better Is It Really?
For most otherwise healthy people with mild to moderate hangovers, drinking fluids and resting is usually sufficient—and significantly cheaper than IV therapy.
Oral Rehydration Options
Effective alternatives to reduce dehydration include:
- Plain water
- Oral rehydration solutions (Pedialyte, DripDrop)
- Low-sugar sports drinks
- Broths and soups
- Coconut water
These options restore balance of fluids and electrolytes effectively over a few hours, even if nutrient absorption is somewhat slower than IV delivery.
When IV Has a Clear Advantage
IV hydration therapy makes the most sense when:
- You’re experiencing severe vomiting and cannot keep fluids down
- Signs of serious dehydration appear (minimal urination, rapid heart rate, extreme dizziness)
- You have a coexisting illness complicating recovery
- You need to function quickly for work or travel obligations
Cost and Convenience Reality Check
| Option | Approximate Cost | Time Investment |
|---|---|---|
| Hangover IV drip | $150-400 | 45-90 minutes at clinic |
| Sports drinks + OTC meds | $10-20 | Available immediately at home |
| Water + rest | Free | Available immediately |
Practical Rule of Thumb
Try at-home measures first. Reserve IV vitamin therapy for more severe cases or when symptoms fail to improve over several hours despite adequate oral hydration.
Evidence-Based Hangover Relief: What Actually Works (With Or Without IVs)
No method instantly erases a hangover—time remains the ultimate healer. However, combining evidence-informed strategies can significantly alleviate hangover symptoms and help you function sooner.
Hydration Strategy
Sip water or an electrolyte drink regularly throughout the morning. Aim for pale yellow urine as your hydration levels indicator. Avoid gulping massive amounts quickly, especially if you have heart or kidney issues—this can stress your system unnecessarily.
Pain and Inflammation Control
Over-the-counter NSAIDs like ibuprofen (400mg) or naproxen can reduce headache and body aches by 30-50% according to some studies. However:
- Avoid NSAIDs if you have ulcers, kidney disease, or allergies to these medications
- Skip acetaminophen (Tylenol) within 24 hours of heavy drinking—it adds stress to your already-taxed liver
Nausea Management
To ease hangover symptoms related to nausea:
- Eat bland foods: toast, crackers, bananas, plain rice
- Try ginger tea or ginger supplements
- Consider medically supervised anti-nausea medications if severe
- Avoid “hair of the dog”—more alcohol simply prolongs toxicity and dehydration
Food and Blood Sugar
A light, balanced meal helps stabilize blood sugar and improve energy. Good options include:
- Eggs (contain cysteine, which supports liver support)
- Whole-grain toast with avocado
- Bananas (restore potassium for muscle function)
- Oatmeal with fruit
Eating on an empty stomach while hungover tends to worsen nausea initially, so start small and increase as tolerated.

Rest and Sleep
Quality sleep is one of the most powerful—and underrated—hangover remedies. Alcohol disrupts REM cycles, leaving you sleep-deprived even after 8 hours in bed. Extra rest, dim lighting, and quiet environments help your body recover and improve mental clarity.
Gentle Movement
A light walk or gentle stretching may improve circulation and mood. However, high-intensity workouts while dehydrated can be dangerous and should wait until you’re fully recovered with normal hydration levels.
Myths to Avoid
- Coffee won’t cure you—it may worsen dehydration and anxiety (those mood swings aren’t helping)
- Energy drinks mask symptoms temporarily while adding sugar and caffeine that can make you feel worse later
- More alcohol delays the inevitable and causes additional damage
How To Prevent Future Hangovers (The Only Real Cure)
Prevention is the only foolproof approach. Once alcohol and its byproducts enter your system, they must be metabolized over time—no treatment changes that fundamental biology.
Moderation Strategies
- Set a drink limit before going out and stick to it
- Pace yourself at roughly one standard drink per hour
- Alternate each alcoholic drink with water or a non-alcoholic beverage
- Stay hydrated throughout the evening
Food Timing
Eat a substantial meal with protein, fat, and complex carbs before or while drinking. Examples:
- Grilled chicken with vegetables and brown rice
- Pasta with meat sauce and salad
- Burger with a side of vegetables
Food slows alcohol absorption, giving your liver more time to process each drink.
Smarter Alcohol Choices
- Choose lighter-colored spirits (vodka, gin, white wine) over darker options
- Avoid mixing multiple types of alcohol in one night
- Skip high-sugar mixed drinks that worsen dehydration and nausea
Sleep Planning
Plan for a full night’s sleep after events involving alcohol. This gives your body more time to process everything and restore normal brain chemistry.
A Word on Frequency
Repeated heavy drinking—even with IV therapy for hangovers—causes cumulative damage to your liver, heart, and brain health over time. The U.S. economy loses an estimated $220 billion yearly to hangover-related lost productivity. If you find yourself needing hangover help regularly, it may be worth discussing your drinking habits with a healthcare professional.
Is IV Hangover Therapy Right For You?
IV therapy is a medical-grade tool, not a lifestyle accessory. Whether it’s appropriate depends on your symptoms, health history, and specific circumstances.
People Who Might Reasonably Consider IV Therapy
- Those with severe dehydration after excessive alcohol consumption
- People experiencing persistent vomiting who can’t keep fluids down
- Anyone needing to function quickly for work, travel, or other obligations
- Individuals already under medical care where IV access exists
People Who Should Be Cautious or Avoid Elective Hangover IVs
- Those with heart failure or kidney disease
- People with uncontrolled high blood pressure
- Anyone with bleeding or clotting disorders
- Those with a history of reactions to IV medications
- Pregnant individuals
What a Safe IV Visit Should Include
- Brief medical history review
- Vital signs check (blood pressure, heart rate)
- Discussion of IV ingredients and any allergies
- Informed consent
- Sterile technique throughout
- Supervision by a licensed professional
Note that most health insurance companies do not cover elective hangover IVs, as they’re considered wellness treatments rather than medically necessary care.
The Bottom Line
View IV therapy as occasional support for particularly rough hangovers—not a license to consume too much alcohol regularly. The treatment addresses symptoms, not the underlying issue of various factors that contribute to excessive drinking.
FAQ
Does IV therapy completely cure a hangover?
No, IV therapy does not “erase” a hangover. It primarily treats dehydration, delivers essential nutrients, and can ease nausea and pain when medications are included. However, your liver still needs hours to process alcohol and its toxic byproducts fully. Even after an IV, you may feel tired or mentally sluggish until the next day. Combining IV support with rest, food, and sleep gives better results than expecting instant, 100% recovery.
How long do hangover IV treatments take to work and how long do the effects last?
Most infusions run 45-90 minutes, and many people notice improvement in headache and dizziness before the drip is finished due to faster absorption and efficient delivery directly into the bloodstream. Benefits like better hydration and reduced nausea typically last through the rest of the day. However, overall fatigue or low mood may take 12-24 hours to fully resolve. Individual responses vary significantly, and lifestyle factors—sleep quality, ongoing hydration, food intake—strongly influence how long relief lasts.
Is it safe to get IV therapy the morning after heavy drinking?
For most generally healthy adults, IV therapy administered by qualified staff in a clean setting is considered low-risk—but it’s still a medical procedure. Key safety checks should include review of your medical history and medications, blood pressure and heart rate assessment, and discussion of allergies or pregnancy. Skip elective IVs and seek urgent medical care if you experience red-flag symptoms like chest pain, severe shortness of breath, confusion, uncontrolled vomiting, or signs of alcohol poisoning.
Can I just drink water instead of getting an IV for a hangover?
For mild to moderate hangovers, most people can fully recover by drinking water or electrolyte drinks, eating nutrient-dense foods, and resting—without needing IV fluids. IV vitamin therapy works faster and bypasses the digestive system, making it useful when someone cannot keep fluids down or is significantly dehydrated. The recommendation: start with oral hydration at home, monitor your health state, and consider IV therapy only if symptoms are more severe or fail to improve over several hours.
How often is it safe to use IV therapy for hangovers?
There’s no universal “safe” frequency—it depends on individual health, kidney function, heart conditions, and what’s in the IV formula. However, if someone finds themselves wanting or needing IV therapy after drinking more than a few times per year, it may signal a need to reassess alcohol use and consult a healthcare professional. IVs should supplement, not replace, long-term strategies to drink moderately and protect overall well being. The nutrient boost from IVs doesn’t undo the cumulative effects of regular heavy drinking on your organs.